Research
February 20, 2026
GDP
U.S. economy grew slower than expected in Q4, pulled lower by government shutdown
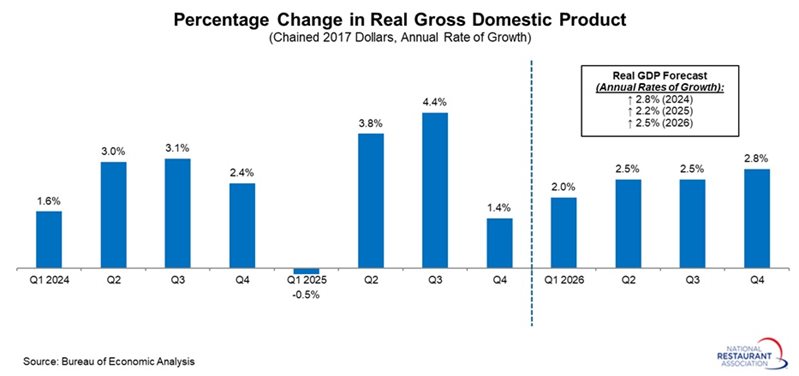
The U.S. economy grew just 1.4% at an annual rate in the fourth quarter, down sharply from 4.4% in the third quarter and well below the consensus forecast of at least 2.5%. Much of this softness reflected the federal government shutdown, which shaved 1.15 percentage points off top-line growth.
Even so, the underlying data show pockets of resilience—particularly in service‑sector consumer spending—though overall activity was weaker than desired. Total consumer spending and fixed investment, a proxy for domestic demand, rose 2.4% at an annual rate in the fourth quarter, easing from 2.9% in the prior quarter.
There were also notable areas of weakness, including softer demand for goods and business investment that, while positive, continues to lag expectations.
Looking ahead, the National Restaurant Association anticipates continued economic expansion, with real GDP projected to rise 2.5% in 2026, a forecast that reflects steady momentum despite persistent downside risks.
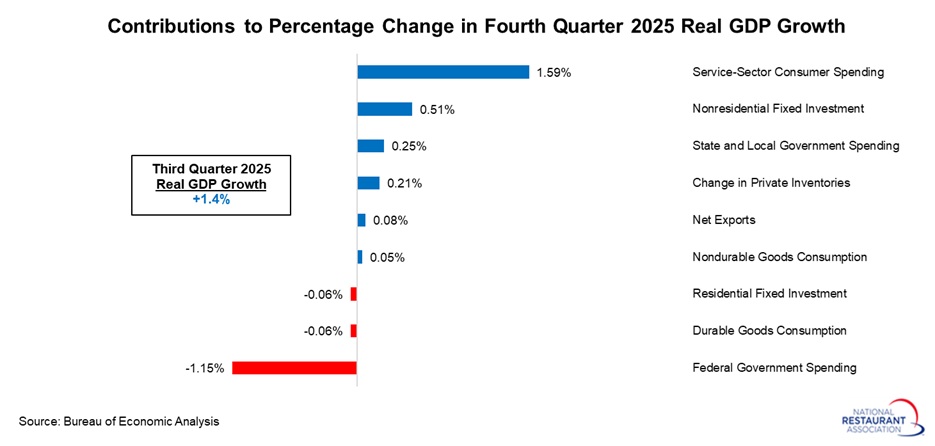
Digging deeper into the data, consumer spending remained uneven, with solid gains in services (+3.4% at an annual rate) offset by essentially flat demand for goods (‑0.1%). Overall, personal consumption expenditures rose 2.4% in Q4, down from 3.5% in Q3, contributing 1.58 percentage points to headline GDP. Even so, spending at foodservices and accommodations subtracted 0.04 percentage points from GDP in Q4, pulling back after contributing positively in each of the previous two quarters.
Investment activity rebounded in Q4, rising 3.8% at an annual rate after being flat in Q3. Fixed investment strengthened from 0.8% growth in Q3 to 2.6% in Q4, with nonresidential fixed investment picking up from 3.2% to 3.7%. Equipment (+3.2%) and intellectual property products (+4.6%) both performed well, while structures investment (‑2.4%) declined for the eighth consecutive quarter. Meanwhile, residential investment (‑1.5%) fell for the fourth straight quarter, and businesses modestly rebuilt inventories after drawing them down over the prior two quarters.
Net exports added 0.08 percentage points to real GDP in Q4, a small increase following robust gains in Q2 and Q3. Despite the positive contribution, both exports (+0.9% at an annual rate) and imports (‑1.3%) were lower in the latest quarter.
Federal government spending was the largest drag on growth, with federal outlays falling at an annualized pace of 16.6% and subtracting 1.15 percentage points from GDP in Q4—an impact driven entirely by the federal government shutdown. In contrast, state and local government spending rose 2.4% in Q4, adding 0.25 percentage points to top‑line real GDP growth.
Even so, the underlying data show pockets of resilience—particularly in service‑sector consumer spending—though overall activity was weaker than desired. Total consumer spending and fixed investment, a proxy for domestic demand, rose 2.4% at an annual rate in the fourth quarter, easing from 2.9% in the prior quarter.
There were also notable areas of weakness, including softer demand for goods and business investment that, while positive, continues to lag expectations.
Looking ahead, the National Restaurant Association anticipates continued economic expansion, with real GDP projected to rise 2.5% in 2026, a forecast that reflects steady momentum despite persistent downside risks.
Digging deeper into the data, consumer spending remained uneven, with solid gains in services (+3.4% at an annual rate) offset by essentially flat demand for goods (‑0.1%). Overall, personal consumption expenditures rose 2.4% in Q4, down from 3.5% in Q3, contributing 1.58 percentage points to headline GDP. Even so, spending at foodservices and accommodations subtracted 0.04 percentage points from GDP in Q4, pulling back after contributing positively in each of the previous two quarters.
Investment activity rebounded in Q4, rising 3.8% at an annual rate after being flat in Q3. Fixed investment strengthened from 0.8% growth in Q3 to 2.6% in Q4, with nonresidential fixed investment picking up from 3.2% to 3.7%. Equipment (+3.2%) and intellectual property products (+4.6%) both performed well, while structures investment (‑2.4%) declined for the eighth consecutive quarter. Meanwhile, residential investment (‑1.5%) fell for the fourth straight quarter, and businesses modestly rebuilt inventories after drawing them down over the prior two quarters.
Net exports added 0.08 percentage points to real GDP in Q4, a small increase following robust gains in Q2 and Q3. Despite the positive contribution, both exports (+0.9% at an annual rate) and imports (‑1.3%) were lower in the latest quarter.
Federal government spending was the largest drag on growth, with federal outlays falling at an annualized pace of 16.6% and subtracting 1.15 percentage points from GDP in Q4—an impact driven entirely by the federal government shutdown. In contrast, state and local government spending rose 2.4% in Q4, adding 0.25 percentage points to top‑line real GDP growth.
.jpg?lang=en-US)