Research
February 16, 2022
Restaurant sales fell for the second consecutive month
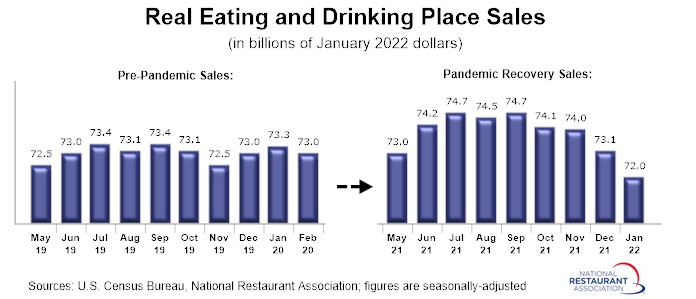
Real sales in January were lower than the volumes posted in each of the 10 months leading up to the pandemic.
Restaurant sales declined for the second consecutive month in January, as the omicron variant negatively impacted business conditions.
Eating and drinking places* registered total sales of $72.0 billion on a seasonally adjusted basis in January, according to preliminary data from the U.S. Census Bureau. That was down from readings of $73.1 billion in November and $72.7 billion in December, and represented the lowest monthly sales volume since June 2021.
In inflation-adjusted terms, restaurant sales registered even more dramatic declines in recent months. After adjusting for menu-price inflation, eating and drinking place sales in January were nearly $3 billion lower than the levels reached in mid-2021.
In addition, real eating and drinking place sales in January were lower than the volumes posted in each of the 10 months leading up to the pandemic.
Omicron variant dampened consumer confidence in dining out
With the omicron variant curtailing business operations for many restaurants, it’s not surprising that sales declined in January.
Eighty-eight percent of restaurants experienced a decline in customer demand for indoor on-premises dining in recent weeks, as a result of the increase in coronavirus cases across the U.S. due to the omicron variant. That’s according to an Association survey of 4,200 restaurant operators fielded January 6-18.
This forced restaurants to take a number of actions: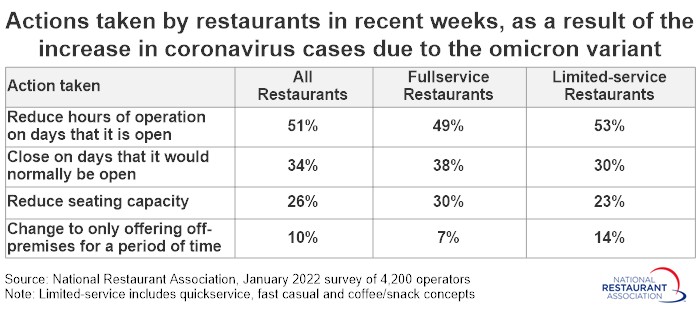
In the same survey, 76% of operators said business conditions for their restaurant were worse in January than they were 3 months earlier. Only 3% said business conditions improved during the last 3 months.
*Eating and drinking places are the primary component of the U.S. restaurant and foodservice industry, which prior to the coronavirus outbreak generated approximately 75 percent of total restaurant and foodservice sales.
Read more analysis and commentary from the Association's chief economist Bruce Grindy.
Eating and drinking places* registered total sales of $72.0 billion on a seasonally adjusted basis in January, according to preliminary data from the U.S. Census Bureau. That was down from readings of $73.1 billion in November and $72.7 billion in December, and represented the lowest monthly sales volume since June 2021.
In inflation-adjusted terms, restaurant sales registered even more dramatic declines in recent months. After adjusting for menu-price inflation, eating and drinking place sales in January were nearly $3 billion lower than the levels reached in mid-2021.
In addition, real eating and drinking place sales in January were lower than the volumes posted in each of the 10 months leading up to the pandemic.

Omicron variant dampened consumer confidence in dining out
With the omicron variant curtailing business operations for many restaurants, it’s not surprising that sales declined in January.
Eighty-eight percent of restaurants experienced a decline in customer demand for indoor on-premises dining in recent weeks, as a result of the increase in coronavirus cases across the U.S. due to the omicron variant. That’s according to an Association survey of 4,200 restaurant operators fielded January 6-18.
This forced restaurants to take a number of actions:
- 51% reduced hours of operation on days that it is open
- 34% closed on days that it would normally be open
- 26% reduced seating capacity
- 10% changed to only offering off-premises for a period of time

In the same survey, 76% of operators said business conditions for their restaurant were worse in January than they were 3 months earlier. Only 3% said business conditions improved during the last 3 months.
*Eating and drinking places are the primary component of the U.S. restaurant and foodservice industry, which prior to the coronavirus outbreak generated approximately 75 percent of total restaurant and foodservice sales.
Read more analysis and commentary from the Association's chief economist Bruce Grindy.