Higher-income households are driving restaurant sales
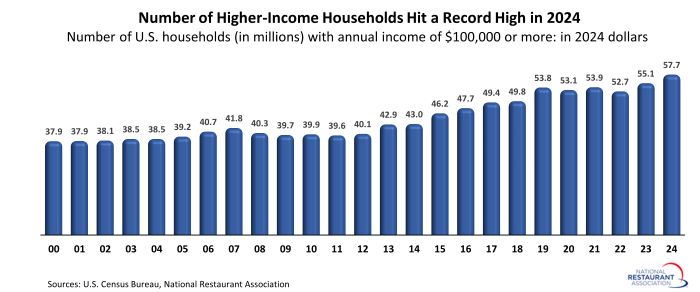
Higher-income households are critical drivers of growth in the restaurant industry, and the good news is that these households surged to new highs during the last 2 years. There were 57.7 million households with annual income of $100,000 or more in 2024, according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau.
That represented an increase of 5 million households from 2022 (on an inflation-adjusted basis), when households with income of $100,000 or more numbered 52.7 million.
The recent upward trend is important, because the number of higher-income households declined during the pandemic. After reaching a peak of 53.8 million in 2019, the number of households with income of at least $100,000 fell to 52.7 million in 2022 (on an inflation-adjusted basis).
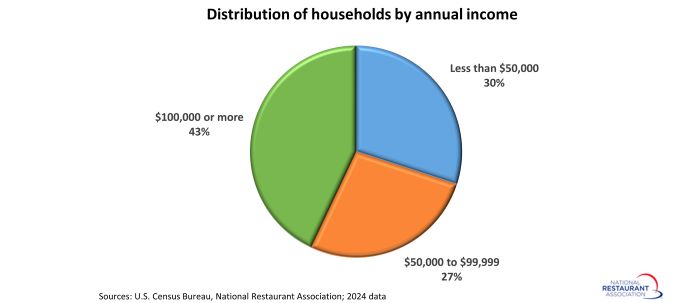
Higher-income households also make up a larger share of total households than they ever have. Households with income above $100,000 represented 43% of all households in 2024, which represented the highest proportion on record.
In comparison, the 40.7 million households with annual income below $50,000 represented 30% of all households in 2024, while the 36.5 million households in the $50,000 - $99,999 income range made up 27% of the total.
Growth in the number of higher-income households is a positive sign for restaurants, as this demographic group represents the majority of spending in the industry. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, households with incomes of $200,000 or higher are responsible for 24% of the total spending on food away from home, while households with incomes between $100,000 and $199,999 account for 35% of industry spending.
Taken together, households with income above $100,000 are responsible for nearly 6 in 10 dollars spent in restaurants. That despite representing only 43% of all households in the United States.
If the positive trend in higher-income households continues, it bodes well for restaurant sales growth in the years ahead.
